C/2001 G1 LONEOS
more info
C/2001 G1 was discovered on 1 April 2001 by the LONEOS as an apparently asteroidal object. At once, its cometary apperance was reported [IAUC 7606, 2001 April 2]. Later, pre-discovery detections by Air Force Maui Optical and Supercomputing observatory (AMOS) from 28 and 29 December 2000 were found.
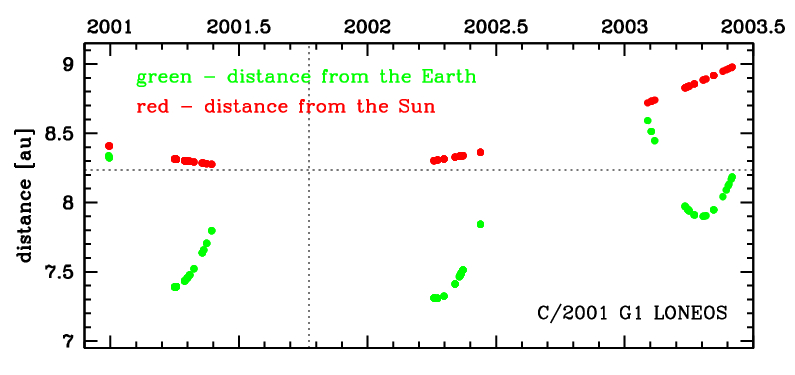
This comet made its closest approach to the Earth on 8 April 2002 (7.309 au), six months after perihelion.
Solution given here is based on data spanning over 2.4 yr in a range of heliocentric distances: 8.41 au – 8.235 au (perihelion) – 8.98 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers small planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system that lead to escape of the comet from the solar system on hiperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbit).
See also Królikowska 2014 and Królikowska and Dybczyński 2017.
This comet made its closest approach to the Earth on 8 April 2002 (7.309 au), six months after perihelion.
Solution given here is based on data spanning over 2.4 yr in a range of heliocentric distances: 8.41 au – 8.235 au (perihelion) – 8.98 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers small planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system that lead to escape of the comet from the solar system on hiperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbit).
See also Królikowska 2014 and Królikowska and Dybczyński 2017.
| solution description | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of observations | 138 | |
| data interval | 2000 12 28 – 2003 06 01 | |
| data type | perihelion within the observation arc (FULL) | |
| data arc selection | entire data set (STD) | |
| range of heliocentric distances | 8.41 au – 8.23 au (perihelion) – 8.98 au | |
| detectability of NG effects in the comet's motion | NG effects not determinable | |
| type of model of motion | GR - gravitational orbit | |
| data weighting | YES | |
| number of residuals | 266 | |
| RMS [arcseconds] | 0.58 | |
| orbit quality class | 1a | |
| previous orbit statistics, both Galactic and stellar perturbations were taken into account | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| previous reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | 35.22 – 37.58 – 39.85 | |
| previous perihelion distance [au] | 510 – 710 – 900 | |
| previous aphelion distance [103 au] | 49.7 – 52.5 – 55.9 | |
| time interval to previous perihelion [Myr] | 3.3 – 3.7 – 4.2 | |
| percentage of VCs with qprev > 20 | 100 | |
| previous_g orbit statistics, here only the Galactic tide has been included | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| previous reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | 37.18 – 40.56 – 44.14 | |
| previous perihelion distance [au] | 12 – 14 – 18 | |
| previous aphelion distance [103 au] | 45.3 – 49.3 – 53.8 | |
| time interval to previous perihelion [Myr] | 3.4 – 3.8 – 4.3 | |
| percentage of VCs with 10 < qprev < 20 | 96 | |
| percentage of VCs with qprev > 20 | 4 | |