C/2017 F2 PANSTARRS
more info
Comet C/2017 F2 was discovered on 31 March 2017 with Pan-STARRS 1 telescope (Haleakala), that is about 8 months before its perihelion passage. This comet was rarely observed until 6 March 2019.
Comet had its closest approach to the Earth on 31 March 2018 (6.070 au), about 4 months after its perihelion passage.
The preferred solution given here is based on data spanning over 1.93 yr in a range of heliocentric distances: 7.10 au – 6.928 au (perihelion) – 7.56 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers moderate planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; these perturbations lead to escape the comet from the planetary zone on a hyperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbits).
Comet had its closest approach to the Earth on 31 March 2018 (6.070 au), about 4 months after its perihelion passage.
The preferred solution given here is based on data spanning over 1.93 yr in a range of heliocentric distances: 7.10 au – 6.928 au (perihelion) – 7.56 au.
This Oort spike comet suffers moderate planetary perturbations during its passage through the planetary system; these perturbations lead to escape the comet from the planetary zone on a hyperbolic orbit (see future barycentric orbits).
| solution description | ||
|---|---|---|
| number of observations | 62 | |
| data interval | 2017 03 31 – 2018 12 12 | |
| data type | perihelion within the observation arc (FULL) | |
| data arc selection | entire data set (STD) | |
| range of heliocentric distances | 7.1 au – 6.93 au (perihelion) – 7.35 au | |
| detectability of NG effects in the comet's motion | NG effects not determinable | |
| type of model of motion | GR - gravitational orbit | |
| data weighting | NO | |
| number of residuals | 112 | |
| RMS [arcseconds] | 0.37 | |
| orbit quality class | 1a | |
| next orbit statistics, both Galactic and stellar perturbations were taken into account | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| next reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | -323.57 – -319.75 – -315.80 | |
| next perihelion distance [au] | 4.639 – 4.669 – 4.7 | |
| synchronous stop epoch [Myr] | 0.966 | S |
| percentage of VCs with qnext < 10 | 100 | |
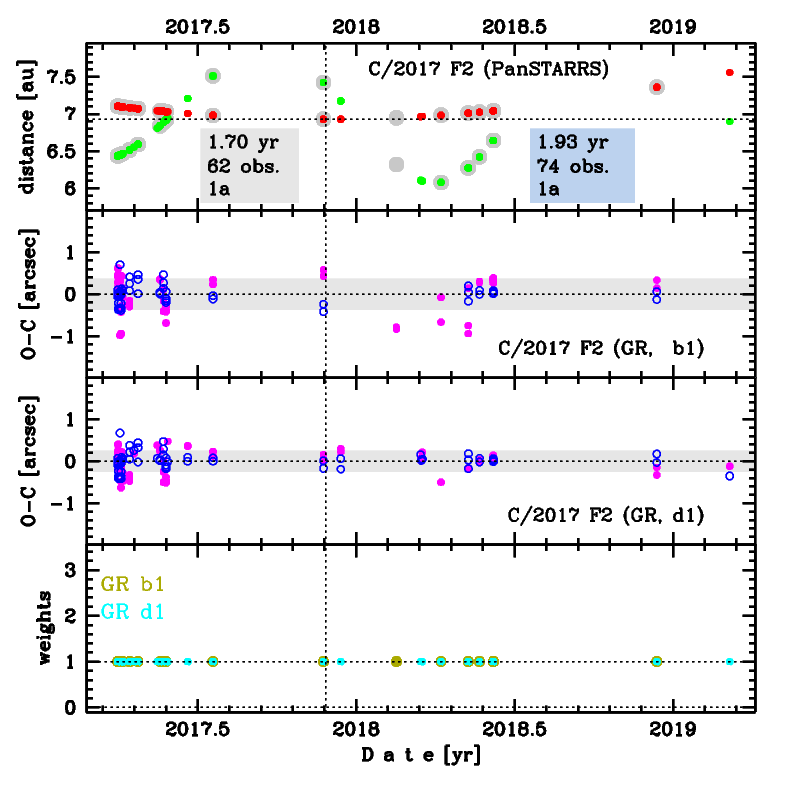
Upper panel: Time distribution of positional observations with corresponding heliocentric (red curve) and geocentric (green curve) distance at which they were taken. The horizontal dotted line shows the perihelion distance for a given comet whereas vertical dotted line — the moment of perihelion passage.
Middle panel(s): O-C diagram for a given solution (sometimes in comparison to another solution available in CODE), where residuals in right ascension are shown using magenta dots and in declination by blue open circles.
Lowest panel: Relative weights for a given data set(s).
Middle panel(s): O-C diagram for a given solution (sometimes in comparison to another solution available in CODE), where residuals in right ascension are shown using magenta dots and in declination by blue open circles.
Lowest panel: Relative weights for a given data set(s).
| next_g orbit statistics, here only the Galactic tide has been included | ||
|---|---|---|
| no. of returning VCs in the swarm | 0 | |
| no. of escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | |
| no. of hyperbolas among escaping VCs in the swarm | 5001 | * |
| next reciprocal semi-major axis [10-6 au-1] | -323.20 – -319.38 – -315.43 | |
| next perihelion distance [au] | 6.169 – 6.183 – 6.197 | |
| synchronous stop epoch [Myr] | 1.02 | S |
| percentage of VCs with qnext < 10 | 100 | |